- Dietary benefits of berries
- Beneficial effects of antioxidants in berries
- Polyphenol antioxidants in berries
- Other dietary benefits of polyphenol antioxidants
Dietary benefits of berries
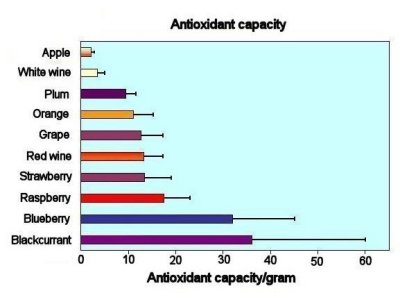
Berries are a good source of dietary fibre, vitamins (such as ascorbic acid =Vitamin C and folic acid = vitamin B9) and essential minerals, such as zinc.
Berries contain amongst the highest high levels of natural antioxidants - which can combat the oxidative damage caused by oxygen-derived free radicals during normal metabolism.
Beneficial effects of antioxidants in berries
Berry extracts are rich in antioxidants that effectively inhibit the oxidation of low density lipoproteins (LDLs) in the blood which can prevent plaque formation and reduce incidence of heart attacks. View poster on 'Dietary Polyphenols and Health' and the implications for Cardiovascular disease (CVD).
The main antioxidants are ascorbic acid and the polyphenols. We are interested in improving the levels of vitamin C and polyphenols in new berry varieties. View poster on 'Increasing the Vitamin C content of blackcurrants'. View poster on 'Rubus and Ribes: Identification of nutritional breeding targets''.
Maintaining the quality and antioxidant potency of berry products during post-harvest storage or processing is also important. View poster on 'Effect of High O2 and N2 Atmospheres on Strawberry Quality'.
Polyphenol antioxidants in berries
We are also investigating the levels of polyphenol antioxidants found in wild blackcurrants, raspberries, strawberries and less well known berries from Northern Europe to discover natural variation that could be tapped to breed new antioxidant-enhanced varieties. View poster on 'Scandinavian Berries as a Nutritionally Relevant Source of Antioxidants'.
We are also analysing polyphenol composition in the progeny of the Glen Moy X Latham raspberry cross which should allow us to link genomic maps and the inheritance of polyphenol composition to help direct future breeding efforts.
Other dietary benefits of polyphenol antioxidants
However, polyphenols also have biological effects beyond their antioxidant potential. The James Hutton Institute has carried out research into some aspects of this area and has initiated research with suitable collaborators to examine other polyphenol effects
Polyphenols in raspberries and strawberries inhibit starch digestion and could influence post-meal blood glucose levels, a known therapeutic route to control non-insulin-dependent (or type 2) diabetes mellitus (NIDDM). View poster on 'Different polyphenolic components of soft fruits inhibit a-amylase and a-glucosidase'
Berry polyphenols also have potent beneficial effects on cardiovascular performance. View poster on 'Cardiovascular - Protective properties of Fruit and Vegetable Extracts'
